Turbulent Flows - آزمایشگاه شبیهسازی دینامیک شارهها و علوم گرمایی cfdtherms
Turbulent Flows
Turbulent separation, which is caused by an adverse pressure gradient, is one of the most important phenomena in fluid dynamics, aerodynamics, and propulsion engineering. Since this phenomenon affects all the properties of the flow, heat transfer is not an exception. Therefore, the study of a case that covers the phenomenon of turbulence, separation, and heat transfer, which are three significant and common phenomena in fluid flow, can be an ideal study for refining the efficacy of equipment designs.
Diffusers in the gas turbines are subject to such flow phenomena. Hence, we have been working to simulate an asymmetric diffuser, which experiences an adverse pressure gradient due to wall expansions. The diffuser was impacted by three-dimensional separation, which frequently reported that the RANS method could not predict the location of separation and the flow field correctly. Thus, the LES method was adopted due to the fact that several studies suggested this method as an appropriate approach.
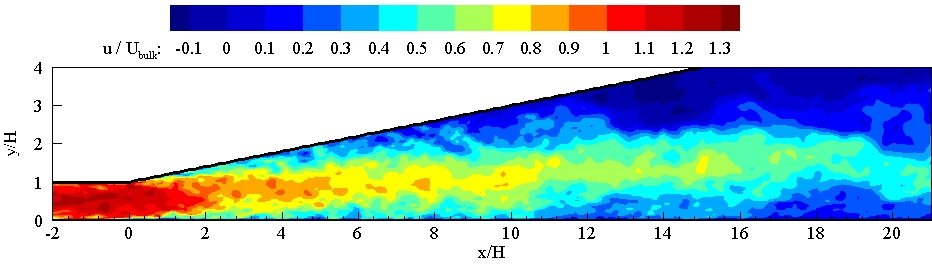
Despite the cost and computational resources, it was worth simulating and studying this diffuser because it can be used as a basic study to understand and analyze more sophisticated geometries, which experience turbulent separation, in the future. In addition, the effect of separation on heat transfer, which is crucial in some equipment such as heat exchangers, combustion chambers, and turbine blades, is studied. The simulation of the diffuser has been performed by the OpenFOAM platform for simulation.
